-
 SrinSoft Inc
SrinSoft Inc
951 W. Yamato Road
Suite 290
Boca Raton, FL 33431
-
 inquiry@enginero.com
inquiry@enginero.com
-
 +1 (614) 468-8976
+1 (614) 468-8976



Construction and engineering projects are evolving and often demanding in nature. These days, as the requirements arise, the project gets complex with the involvement of so many moving parts; designs, regulations, and construction teams working simultaneously, clear communication is more important than ever.
Working with complex designs requires effective collaboration with every stakeholder and respective designers. To tackle this, one such tool is getting vital these days, RFI, known as Request for Information, helps you keep everything aligned and maintain a smooth workflow.
RFIs help teams resolve queries effectively, communicate the backlogs, request any clarification or technical information, and most importantly, quickly resolve issues within a shorter period. As the construction and engineering designs are digitized, and most of the workflows are automated, RFI has become more sophisticated, transitioning from manual tracking systems to automated platforms that streamline communication and decision-making.
This guide will look at the RFI process, the role technology can have in changing the way to manage RFIs are managed, and how to develop a better workflow that can enhance project delivery. Let's now look at how mastering RFI management can improve your project delivery!
A Request for Information (RFI) is a formal document used in construction and engineering projects to clarify uncertainties related to drawings, technical specifications, contractual documents, or any specific need. RFIs are generally initiated by contractors or subcontractors to obtain information from technical teams such as architects, designers, and other stakeholders.
In general, an RFI is used to:
RFIs seem to be simple but can be critical as the queries includes complex issues sometimes, and will affect the processes if not addressed properly, leading to do reworks, delays, costly errors, and much more.
In Construction and Engineering, especially while dealing with designs and models, RFI plays a crucial role. RFIs eliminate the communication gap between different stakeholders like architects, structural engineers, contractors, MEP designers, and other stakeholders. This helps a lot for the field engineers or contractors, when there is a lag in information or a need to resolve specific issues in design, contractors raise an RFI request to the respective design teams.
Sometimes, an RFI also serves as a mode of communication to share views and improve the project design. Similarly, when it comes to production and manufacturing, engineers from the shop floor often face issues with designs, materials, and processes. RFI, again, solves this issue, allowing them to contact the designers when an issue persists.
Also, in industries driven by precision and compliance, effective RFI management is a critical part of quality assurance, regulatory adherence, and efficient collaboration across multidisciplinary teams.
The RFI process is an organized workflow that gives project teams a means to discover, record, and correct gaps or uncertainties in technical information. In engineering and other technical fields, including aerospace, energy, manufacturing, oil & gas, transportation, and infrastructure, the RFI process allows teams to progress with the best information possible that is valid, accurate, recent, and verified.
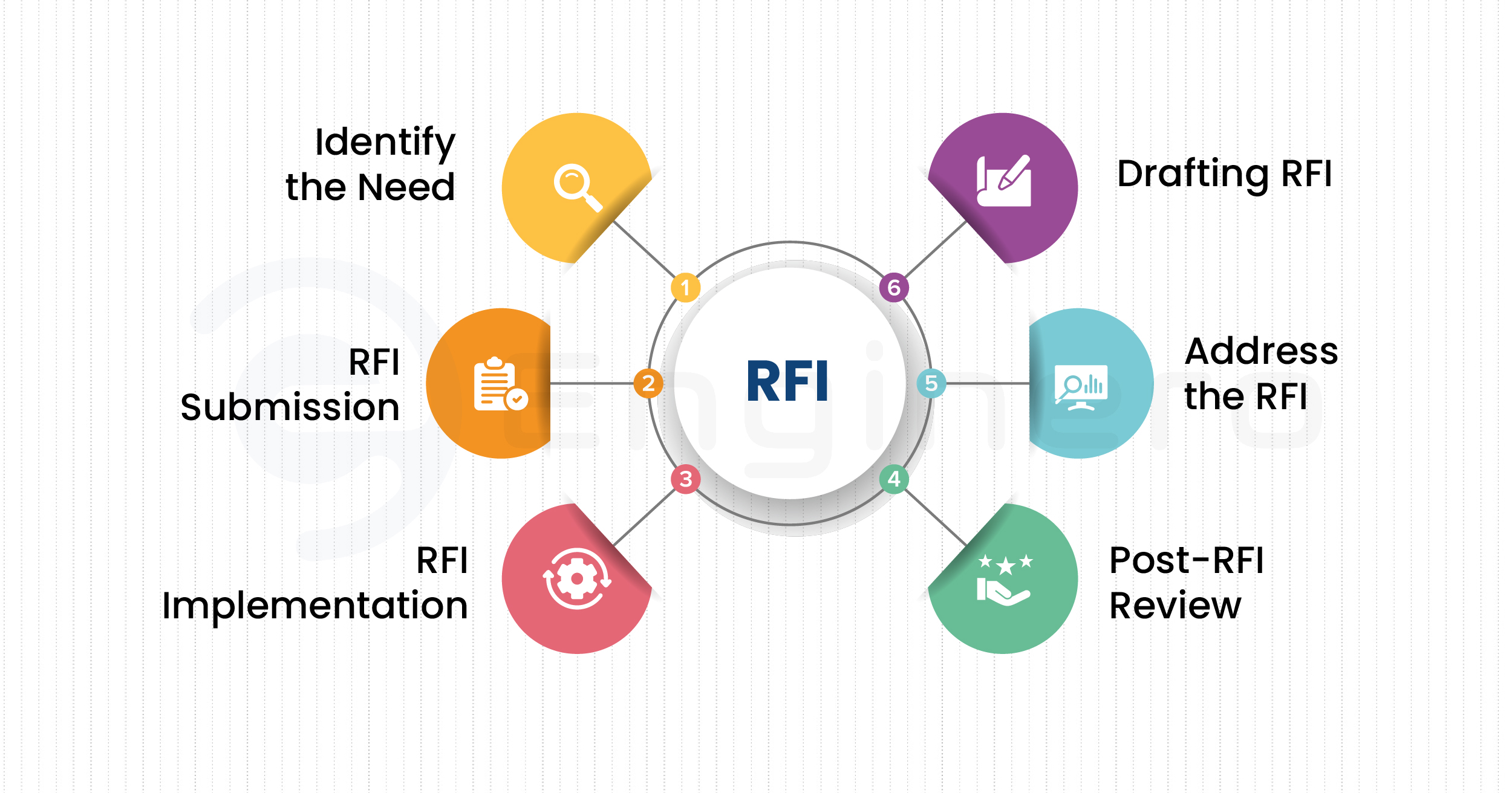
Unlike casual communication, RFIs produce a record that is traceable, which reduces errors, validates compliance and industry standards, and provides evidence of quality control through the life of the project.
An RFI process starts with a need, whether it could be a need for information or issue clarification from a designer, contractor, or any other stakeholders. These are the most common needs:
After knowing the needs, develop a formal RFI document. This should be clear, specific, and solution-oriented. A well-structured RFI must include these key items:
The main goal here is to eliminate the issue, and the request should be clear enough so that it takes less time and effort to address the issue effectively.
Once the RFI is drafted, submit it to the respective project members through the platform where your organization manages project-related activities and designs. It is advised to attach the related files to the RFI and provide access to them. Ensure that the respective project leads will be informed about each project stage. RFI routing can also entail the inclusion of Compliance officers, ensuring any documentation adheres to regulatory standards.
After submission, RFIs are properly examined by the project heads or the respective member (if submitted directly to the accountable person). At this stage, the assigned person works on the RFI and provides a solution to it.
Here, the RFI assignee will be clarifying the design intent, providing the missing data or updated one, accepting/rejecting the proposed alternatives, or any other requested information or suggestions.
Timing is important, as if you respond late, the workflow can become "bottlenecked," causing lost productive time or delaying projects. Many organizations have specific response times to follow and escalate overdue RFIs.
The party that made the request takes action once a suitable response has been received. This could mean:
The RFI is now officially closed, and the outcome is noted in the project documentation system. In some instances, the RFI can also have an initiation of change control or official revisions to the design.
In some organizations, closed RFIs are regularly reviewed as part of the continuous improvement process. Trends are reviewed to identify: .
By studying RFIs, teams can examine the problems and try to reduce the number of RFIs in their future projects, resulting in shorter turnaround times and better efficiency.
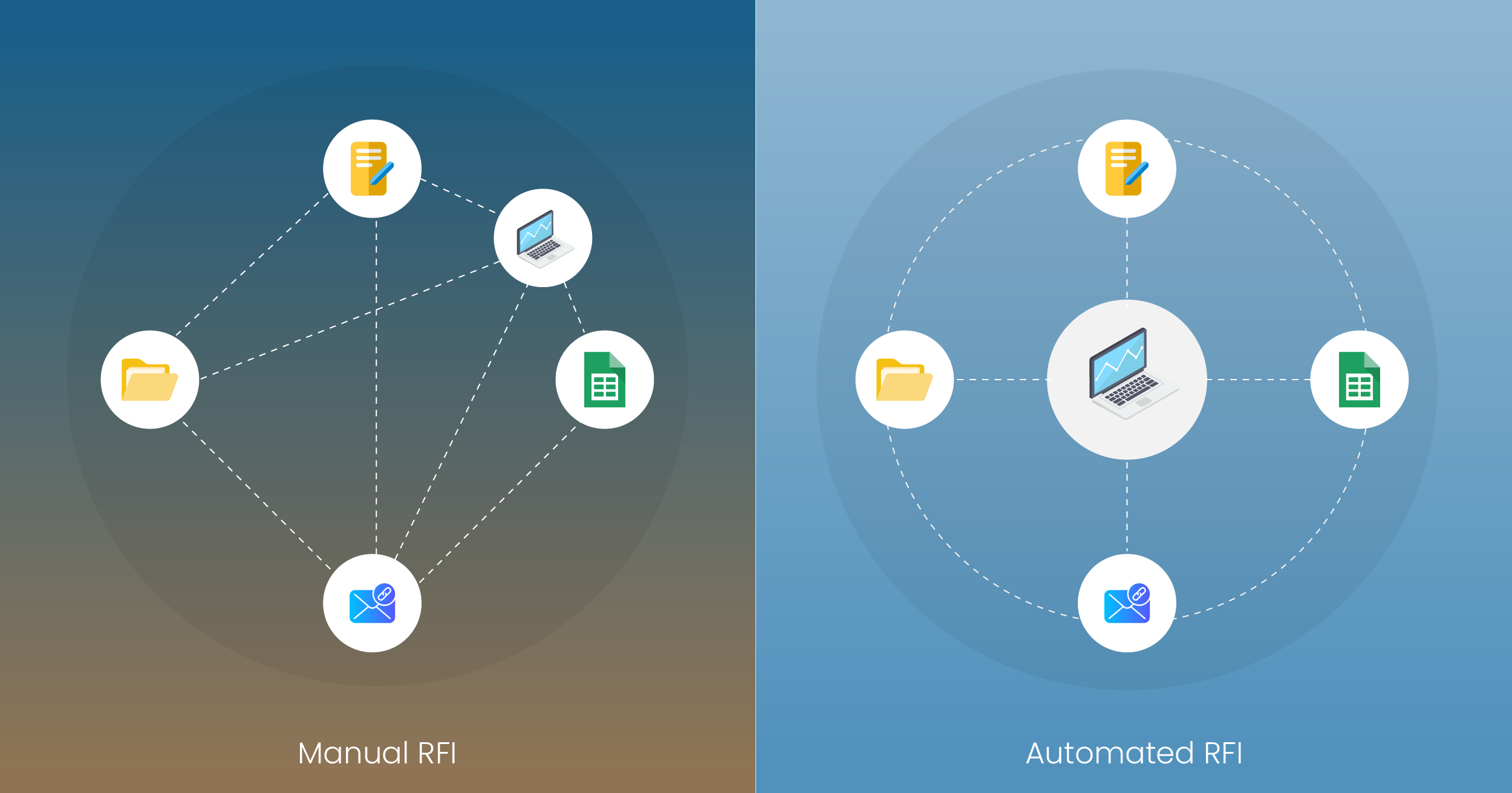
Manual RFI management usually uses spreadsheets, emails, and paper forms to submit, acquire, and track RFIs. RFIs typically have lengthy timeframes before receipt of responses, and reduction of timeliness is further amplified by lost documentation, poorly controlled RFIs, poor communication, and teamwork that lacks accountability.
Getting to the details of specific RFIs can become incredibly challenging, leading to further delays and potential process errors. Automated RFI systems, in contrast, are based on digital platforms that funnel all RFI submissions through one source, thereby improving the process, notifying users in real-time of RFI progress and history, allowing for deadline reminders, and reporting to help identify trends in project completion.
Automated RFI systems allow users to associate an RFI directly to a drawing or document within the project context, thereby reducing the chance of miscommunication and improving overall productivity and escalating decision-making for all project teams.
Despite the advancements in technology and automation, RFI management still encounters several persistent challenges that can impact project efficiency,
RFIs that are vague, or missing details can lead to confusion or delay in the response to the RFI request. As a result, it may lead to miscommunication between contractors, architects, and engineers.
A delayed RFI response can cause a work stoppage on the job site until their request is answered. This can become costly for the contractors, leading to the need to redo work and causing significant delays.
Even with many contractors utilizing many different industry-specific software packages, tracking the status of RFI's, as well as previous RFI's can only be achieved in a manual format, leading to inefficiencies and lost information.
Poorly written RFIs will lead to miscommunication between parties that resulting in mistakes that potentially delay the project schedule and/or negatively affect the expenditure of the project.
Large-scale projects generate a high volume of RFIs, making it challenging to prioritize urgent requests and manage the flow of information. This makes it challenging to figure out the immediate requirements and transfer the important information.
A streamlined RFI workflow helps keep your projects on track by reducing delays and ensuring clear communication. Here are the key steps to building an effective process:
Standardize the Format: Develop a standardized RFI format that includes the submission date, RFI description, drawing reference, priority level, and any attachments. This standardization will reduce communication issues and improve the speed of review.
Define Responsibilities: Identify roles and responsibilities for each stage of the RFI process. In most cases, the contractor submits, the designer or engineer responds, and the project manager monitors and follows up on the response.
Create Timeframes Based on RFI Priority: Not every RFI is an immediate response. Use a high, medium, or low priority system, and your answer timeframe should be consistent with its priority level. This means that a critical RFI will be responded to quickly, while other RFIs will simply be responded to as per the flow.
Keep Everything Organized and Trackable: Use a single source of truth to track your RFIs. This allows the stakeholders to stay coordinated, avoids any duplicate RFIs, and ensures there is no lag.
Each RFI represents an opportunity to identify errors, clarify ambiguities, and prove communications that can be leveraged later for disputes and changes in scope. Also, RFIs are critical tools for risk mitigation. Here are a few ways how RFIs help in risk management,
One of the most valuable aspects of RFIs is their capability of pointing out inconsistencies in designs or specifications before they turn into physical work. Being able to identify inconsistencies early on prevents rework, and it allows for all of the risk to be addressed during planning, not during the date construction starts.
RFIs serve as a paper trail. If a claim or legal dispute arise, RFIs show that a contractor tried to clarify the situation and had official guidance. Documentation protects everyone and often gets used to substantiate defences against claims of negligence, changes that were not authorized, or breach of contract.
Patterns in RFI data can indicate systemic risks. Project managers can take initiative to investigate issues or address broader issues before they manifest into greater problems. By looking at RFI patterns, project teams can identify aspects that need more detailed investigation and potential adjustment.
In some instances, the response to an RFI introduces a change that impacts budget, schedule, or scope. Because an RFI is a formal record, it can be linked directly to any change orders or scope changes, having a direct logical progression to this change. Without the RFI, these changes can occur informally, without authorization, amplifying risk massively.
Assumptions can be one of the greatest risks in construction. If a field crew assumes a detail and moves forward with construction, then every outcome could be unanticipated. RFIs eliminate assumptions by formalizing the need for clarification and establishing that all solutions are traceable and visible for the whole team.
Early and effective use of RFIs can reduce litigation risk, minimize delays, and improve cost forecasting.
Enginero is a comprehensive construction design management platform, allows your team to have better coordination workflows, provides streamlined communications & shows improved collaboration between different stakeholders.
Enginero offers a unified environment for teams to collaborate, coordinate, and manage project data effectively. One of its standout features is the effective RFI management, which facilitates streamlined communication and resolution of issues. Let’s check out a few standout features of Enginero’s RFI management.
Integrated Model Management: Manage all your project models, drawings, and related documents directly within Enginero. You can view these designs and interact with them without opening your native design software.
Intelligent RFI Creation and Management: Enginero users can create RFI requests directly from the interactive model viewer or their native design software with the help of Enginero plugins. Within Enginero, you can create the following RFIs and elevate them directly to the respective project members.
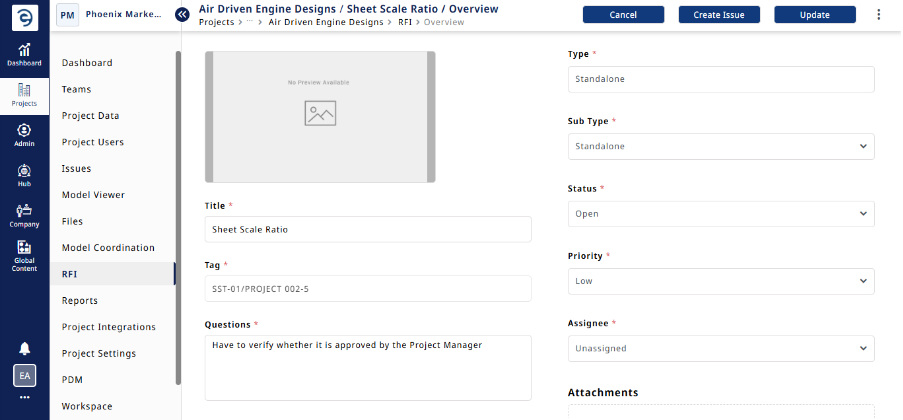
Standalone RFIs are general queries related to the project, whether it could be related to clarification on a construction detail which are not clearly defined in the drawings, seeking approval for a product substitution, confirming code compliance strategies, or any other general query.
An Element-based RFI is specifically linked to a model element; this could be a wall, beam, door, pipe, or any other physical component in the 3D model. The query is about or related to how that element is defined, placed, constructed, or interpreted.
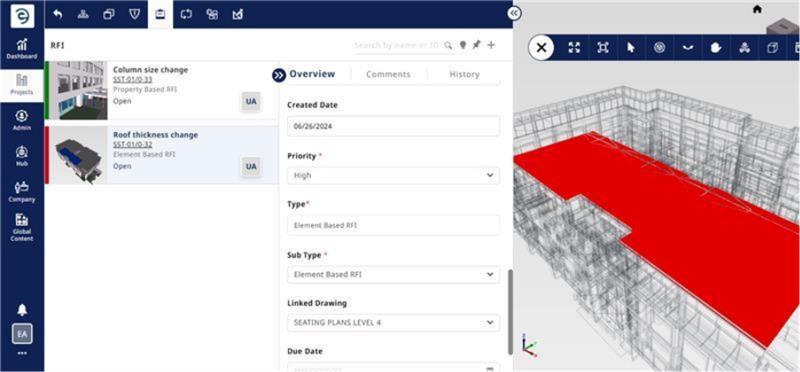
A Property-based RFI is related to metadata or attributes associated with an element, part, or assembly. These properties could include material, thickness, fire rating, manufacturer, load-bearing status, etc.
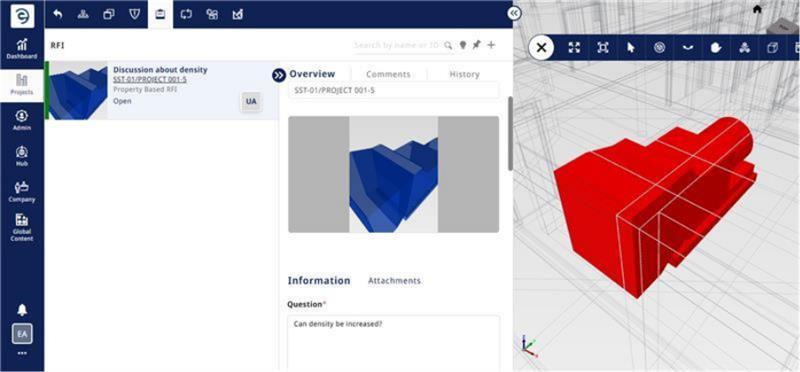
An Issue-based RFI is elevated from an existing coordination issue, clash, or issue identified in the design. It elevates a model coordination or design conflict into a formal RFI, requiring resolution and often approval.
A Markup-based RFI arises from annotations, or markups made directly on 2D construction drawings. These RFIs are typically raised when there's a discrepancy, a missing detail, ambiguity spotted while reviewing 2D sheets or while providing any suggestions.
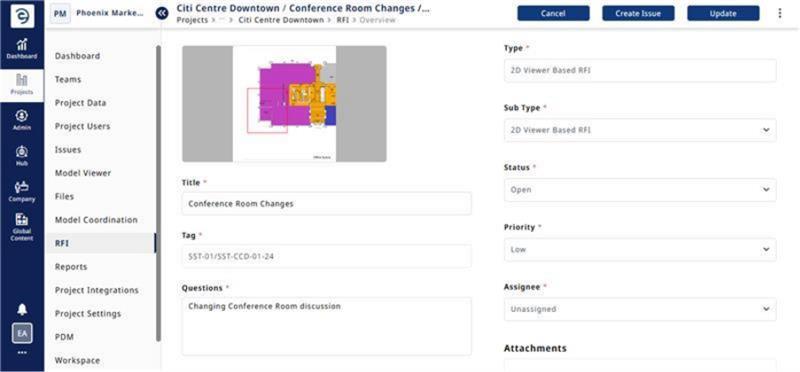
The RFI initiator can directly assign it to the respective user and provide a detailed description of the RFI, along with the deadline and expected outcomes.
Customized Workflows: Project managers can set a proper and customized workflow for each project. As per the needs, you can create different statuses and integrate them into the workflows. As part of the workflow, Enginero sends automated notifications to stakeholders based on workflow status changes. This reduces the chances of delays and helps keep teams on track by reminding them of approaching deadlines.
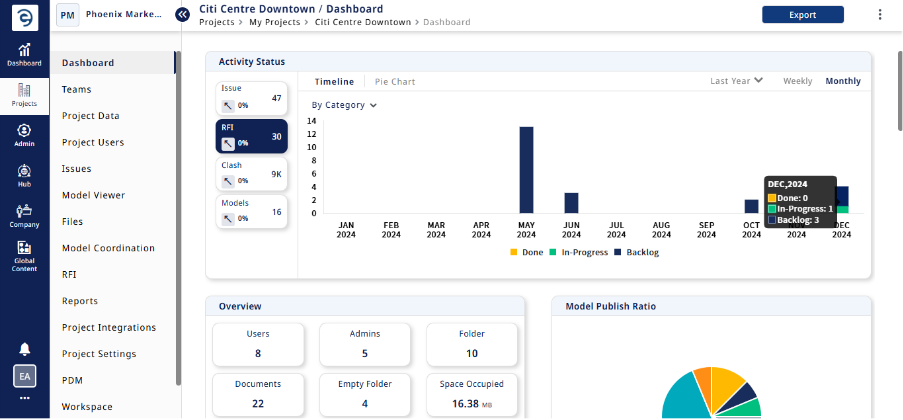
Dashboard Analytics and Report Scheduling: Enginero's powerful Dashboard Analytics gives project managers instant visibility to RFI status and all other project information. This helps your team keep on top of the project, realize where the bottlenecks are, and start making informed data decisions throughout the project. With Enginero, project managers are also able to schedule reports, which means the reports can be generated automatically and sent to the relevant stakeholders, whether it is a weekly status report or a monthly performance report on the team. Project managers can set up automatic reporting for their RFIs as well as all metrics about their project.
Wrapping up, in the construction and engineering sectors, RFI management plays an essential role in communication, workflow, and the successful outcome of projects. As projects grow and become more complex, it is more important than ever to be able to quickly understand ambiguities, fix problems, and track critical information, all while being able to share this information with all relevant project stakeholders.
Automating this process, by utilizing a product like Enginero, and having a simple structured process for handling RFIs will help to reduce construction project delays, errors and create a better working relationship and share knowledge across all stakeholders.
By changing your approach to managing RFIs, you will be implementing the foundations of more productive and more efficient future projects.
It is time to improve the way we manage RFIs to take control of our project outcomes and ensure our project's success.